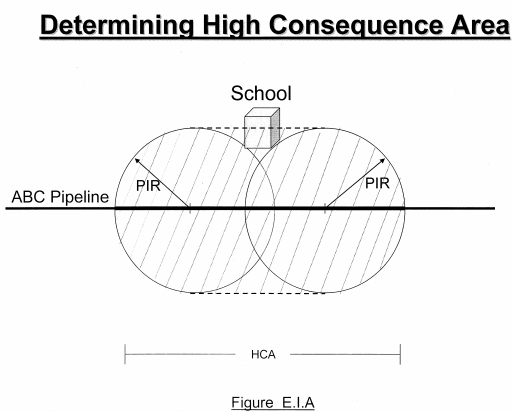
I. Guidance on Determining a High Consequence Area
To determine which segments of an operator's transmission pipeline system are covered for purposes of the integrity management program requirements, an operator must identify the high consequence areas. An operator must use the methods defined in paragraphs (1) or (2) of subdivision (f) of section 255.903 of this Part to identify a high consequence area. An operator may apply one method to its entire pipeline system, or an operator may apply one method to individual portions of the pipeline system. (Refer to Figure 1 below for a diagram of a high consequence area).

II. Guidance on Assessment Methods and Additional Preventive and Mitigative Measures for Transmission Pipelines
(a) Table 1 below gives guidance to help an operator implement requirements on additional preventive and mitigative measures for addressing time dependent and independent threats for a transmission pipeline operating below 30% SMYS not in a High Consequence Area (i.e. outside of potential impact circle) but located within a Class 3 or Class 4 Location.
(b) Table below 2 gives guidance to help an operator implement requirements on assessment methods for addressing time dependent and independent threats for a transmission pipeline in a High Consequence Area.
(c) Table 3 below gives guidance on preventative & mitigative measures addressing time dependent and independent threats for transmission pipelines that operate below 30% SMYS, in High Consequence Areas.
Table 1
Preventive and Mitigative Measures for Transmission Pipelines Operating Below 30% SMYS not in HCAs but in Class 3 and 4 Locations
|
|
Existing Part 255 Requirements |
|
|
|
(Column 1) Threat |
(Column 2) Primary |
(Column 3) Secondary |
(Column 4) Additional (to 255 requirements) Preventive and Mitigative Measures |
|
External Corrosion |
455(Gen. Post 1971) 457(Gen. Pre-1971) 459-(Examination) 461-(Ext. Coating) 463-(CP) 465-(Monitoring) 467-(Elect isolation) 469-(Test Stations) 471-(Test Leads) 473-(Interference) 479-(Atmospheric) 481-(Atmospheric) 485-(Remedial) 705-(Patrol) 706-(Leak Survey) 711-(Repair-gen.) 717-(Repair perm.) |
603(Gen Oper'n) 613-(Surveillance) |
For Cathodically Protected Transmission Pipeline: · Perform semi-annual leak surveys.
For Unprotected Transmission Pipelines or for Cathodically Protected Pipe where Electrical Surveys are Impractical: · Perform quarterly leak surveys |
|
Internal Corrosion |
475-(Gen IC) 477-(IC monitoring) 485-(Remedial) 705-(Patrol) 706-(Leak Survey) 711-(Repair gen.) 717-(Repair perm.) |
53(a)-(Materials) 603-(Gen Oper'n) 613-(Surveillance) |
· Perform semi-annual leak surveys. |
|
3rd Party Damage |
103-(Gen. Design) 111-(Design factor) 317-(Hazard prot) 327-(Cover) 614-(Dam.Prevent) 616-(Public education) 705-(Patrol) 707-(Line markers) 711-(Repair-gen.) 717-(Repair - Perm) |
615-(Emerg. Plan) |
· Participation in state one-call system
· Use of qualified operator employees and contractors to perform marking and locating of buried structures and in direct supervision of excavation work,
AND
Either monitoring of excavations near operator's transmission pipelines, or bi-monthly patrol of transmission pipelines in class 3 and 4 locations. Any indications of unreported construction activity would require a followup investigation to determine if mechanical damage occurred. |
Table 2
Assessment Requirements for Transmission Pipelines in HCAs
(Re-assessment intervals are the maximum allowed)
|
Re-Assessment Requirements (see Note 3) |
||||||
|
|
At or Above 50% SMYS |
Below 30% SMYS |
||||
|
Baseline Assessment Method (See Note 3) |
Max Re-Assessment Interval |
Assessment Method |
Max Re-Assessment Interval |
Assessment Method |
Max Re-Assessment Interval Assessment Method |
|
|
Pressure Testing |
7 |
CDA |
7 |
CDA |
Ongoing |
Preventive & Mitigative (P&M) Measures (See Table 3), (See Note 2) |
|
10 |
Pressure Test or ILI or DA |
|
|
|||
|
|
Repeat inspection cycle every 10 years |
15 (See Note 1) |
Pressure Test or ILI or DA (See Note 1) |
|||
|
|
|
Repeat inspection cycle every 15 years |
20 |
Pressure Test or ILI or DA |
||
|
|
|
|
Repeat inspection cycle every 20 years |
|||
|
In-Line Inspection |
7 |
CDA |
7 |
CDA |
Ongoing |
Preventive & Mitigative (P&M) Measures (See Table 3), (See Note 2) |
|
10 |
ILI or DA or Pressure Test |
|
|
|||
|
|
Repeat Inspection Cycle every 10 years |
15 (See Note 1) |
ILI or DA or Pressure Test (see Note 1) |
|||
|
|
|
Repeat Inspection cycle every 15 years |
20 |
ILI or DA or Pressure Test |
||
|
|
|
|
|
Repeat inspection cycle every 20years |
||
|
Direct Assessment |
7 |
CDA |
7 |
CDA |
Ongoing |
Preventive & Mitigative (P&M)Measures (See Table 3), (See Note 2) |
|
10 |
DA or ILI or Pressure Test |
|
|
|
||
|
|
Repeat inspection cycle every 10 years |
15 (See Note 1) |
DA or ILI or Pressure Test (see Note 1) |
|
||
|
|
|
Repeat inspection cycle every 15 years |
20 |
DA or ILI or Pressure Test |
||
|
|
|
|
Repeat inspection cycle every 20years |
|||
Operator may choose to utilize CDA at year 14, then utilize ILI, Pressure Test, or DA at year 15 as allowed under ASME B31.8S
Operator may choose to utilize CDA at year 7 and 14 in lieu of P&M
Operator may utilize "other technology that an operator demonstrates can provide an equivalent understanding of the condition of line pipe"
Table 3
Preventive & Mitigative Measures addressing Time Dependent and Independent Threats for
Transmission Pipelines that Operate Below 30% SMYS, in HCAs
|
Threat |
Existing 255 Requirements |
Additional (to 255 requirements) Preventive & Mitigative Measures |
|
|
Primary |
Secondary |
||
|
External Corrosion |
455-(Gen. Post 1971) 457-(Gen. Post 1971) 459-(Examination) 461-(Ext. Coating) 463-(CP) 465-(Monitoring) 467-(Elect. Isolation) 469-(Test Stations) 471-(Test Leads) 473-(Interference) 479-(Atmospheric) 481-(Atmospheric) 485-(Remedial) 705-(Patrol) 706-(Leak Survey) 711-(Repair - gen) 717-(Repair perm.) |
603-(Gen. Oper) 613-(Surveillance) |
For Cathodically Protected Transmission Pipelines:
· Perform an electrical survey (i.e. indirect examination tool/method) at least every 7 years. Results are to be utilized as part of an overall evaluation of the CP system and corrosion threat for the covered segment. Evaluation shall include consideration of leak repair and inspection records, corrosion monitoring records, exposed pipe inspection records, and the pipeline environment.
For Unprotected Transmission Pipelines or Cathodically Protected pipe where Electrical Surveys are Impracticable:
· Conduct quarterly leak surveys AND · Every 1 ½ years, determine areas of active corrosion by evaluation of leak repair and inspection records, corrosion monitoring records, exposed pipe inspection records, and the pipeline environment. |
|
Internal Corrosion |
475-(Gen IC) 477-(IC Monitoring) 485-(Remedial) 705-(Patrol) 706-(Leak Survey) 711-(Repair - gen) 717-(Repair perm.) |
53(a)-(Materials) 603-(Gen. Oper) 613-(Surveil) |
· Obtain and review gas analysis data each calendar year for corrosive agents from transmission pipelines in HCAs,
· Periodic testing of fluid removed from pipelines. Specifically, once each calendar year from each storage field that may affect transmission pipelines in HCAs, AND
· At least every 7 years, integrate data obtained with applicable internal corrosion leak records, incident reports, safety related condition reports, repair records, patrol records, exposed pipe reports, and test records. |
|
3rd Party Damage |
103-(Gen. Design) 111-(Design Factor) 317-(Hazard Prot) 327-(Cover) 614-(Dam. Prevent) 616-(Public Educat) 705-(Patrol) 707-(Line Markers) 711-(Repair gen.) 717-(Repair perm.) |
615-(Emer. Plan) |
· Participate in state one-call system,
· Use of qualified operator employees and contractors to perform marking and locating of buried structures and in direct supervision of excavation work, AND
· Either monitoring of excavations near operators transmission pipelines, or bi-monthly patrol of transmission pipelines in HCAs or class 3 and 4 locations. Any indications of unreported construction activity would require a follow up investigation to determine if mechanical damage occurred. |
Historical Note
Sec. Filed eff. April 8, 2005.